#
Focus Areas and Guiding Principles
Part II
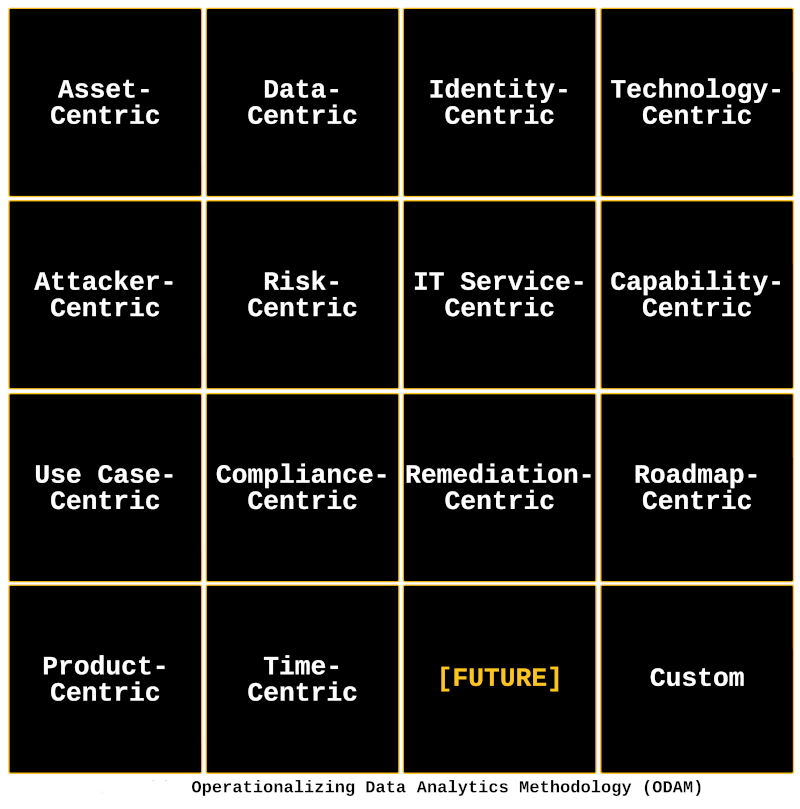
An asset-centric approach focuses on protecting the hardware and software assets of an organization. This may involve identifying and prioritizing the most critical assets, implementing controls and technologies to protect them, and monitoring for and responding to threats that may compromise those assets.
A data-centric approach focuses on protecting the data of an organization. This may involve implementing controls and technologies to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, as well as implementing policies and procedures to govern the handling and use of data.
An identity-centric approach focuses on protecting the identities of individuals within an organization. This may involve implementing strong authentication and access controls, as well as implementing identity and access management (IAM) systems and processes to govern the use of identities.
A technology-centric approach focuses on implementing and maintaining the technologies and systems needed to protect data and ensure uptime. This may involve selecting and implementing appropriate technologies, as well as developing and implementing maintenance and support processes to ensure the ongoing health and performance of those systems.
An attacker-centric approach focuses on understanding and defending against the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers. This may involve implementing controls and technologies designed to detect and prevent attacks, as well as developing and implementing incident response plans to address attacks that do occur.
A risk-centric approach focuses on identifying and mitigating the risks facing an organization. This may involve conducting risk assessments to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, and implementing controls and technologies to address those risks.
An IT service-centric approach focuses on ensuring the availability and performance of the IT services needed to support the business. This may involve implementing monitoring and performance management tools, as well as developing and implementing processes to ensure the availability and reliability of those services.
A capabilities-centric approach focuses on identifying and implementing the capabilities needed to protect data, keep systems up, and ensure maximum uptime. This may involve identifying the specific capabilities that are needed to support the business, and implementing technologies and processes to deliver those capabilities.
A use cases-centric approach focuses on identifying and addressing the specific use cases that are most important to the business. This may involve identifying the specific needs and requirements of different business units or stakeholders, and implementing technologies and processes to support those use cases.
A compliance-centric approach focuses on ensuring that the organization is compliant with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This may involve implementing controls and processes to meet specific compliance requirements, as well as establishing policies and procedures to ensure ongoing compliance.
A remediation-centric approach focuses on identifying and addressing issues or problems as they arise. This may involve implementing monitoring and alerting systems to detect issues, as well as developing and implementing processes to quickly resolve those issues.
A roadmap-centric approach focuses on establishing a long-term plan for protecting data, keeping systems up, and ensuring maximum uptime. This may involve developing a roadmap that outlines the specific steps and actions needed to achieve these goals, as well as establishing timelines and milestones to track progress.
A product-centric approach focuses on implementing specific products or technologies to support the organization's efforts to protect data, keep systems up, and ensure maximum uptime. This may involve selecting and implementing appropriate products or technologies, as well as developing and implementing processes to maintain and support those products/
A time-centric approach to data, cybersecurity, and analytics would focus on the urgency and critical timelines that need to be met, such as deadlines for audits or requirements from cybersecurity insurance companies. This approach would prioritize and address the most pressing concerns and needs in a timely manner.
A zero-trust centric approach is based on the premise that organizations should not trust any user, device, or network by default, and that all access should be authenticated and authorized before being granted. This approach may involve implementing technologies such as multi-factor authentication, network segmentation, and micro-segmentation to secure access to systems and data.
The best approach for your organization will depend on your specific needs and goals. It may be helpful to consider a combination of these approaches, or to customize an approach that is tailored to the unique needs of your organization.