#
Essentials in Analytics Operations
Part IV
#
Data
#
Data Storage Options for Business Analytics
Data storage is a critical component of any business analytics strategy. A data warehouse is a repository of data that is organized and structured to support business analysis. However, there are other options available, such as data lakes and reservoirs, which offer different capabilities and features. It is important for businesses to choose the data storage option that best fits their needs and goals. Some considerations to keep in mind include the ability to access data from various locations, the ability to integrate with different analytics platforms, and the overall cost and scalability of the solution. In order to ensure that your business can effectively leverage data analytics, it is essential to carefully evaluate and choose the right data storage option.
#
The Importance of Data Management in a Data Strategy
Effective data management is crucial for any organization looking to leverage data to drive business success. It involves the planning and execution of processes and systems that ensure the accurate, accessible, and usable storage of data. This includes activities such as data collection and storage, data integration, data cleansing and quality management, data security, and data governance. A well-designed data management system is necessary for supporting the use of data to inform decision-making and drive business actions, and is an essential component of a successful data strategy. Therefore, it is important to consider data management as a key part of any data strategy planning process
#
The Importance of Data Architecture in a Data Strategy
Data architecture is a crucial aspect of a data strategy, as it determines the structure and organization of the data system or ecosystem that supports the data strategy. It includes the design of data models, the relationships between data elements, and the physical implementation of data storage and processing systems. A well-designed data architecture is essential for ensuring that data is accurate, accessible, and usable within an organization, and is a key factor in the successful implementation of a data strategy.
There are two main categories of data architecture: logical data architecture, which defines the logical structure and relationships of data, and physical data architecture, which defines the physical structure and implementation of data storage and processing systems. Both are important considerations when designing and implementing a data strategy.
Effective data architecture plays a critical role in supporting the effective management and use of data within an organization. It helps to ensure that data is integrated, stored, and secured in a way that supports the organization's business goals, and enables the effective use of data to inform decision-making and drive business actions. As such, data architecture should be an integral part of any data strategy planning process.
#
Data Architecture Frameworks
Data architecture frameworks are models or frameworks that provide a structure and approach for designing and organizing a data architecture. These frameworks typically include guidelines and best practices for areas such as data modeling, data storage, data integration, data governance, and data security.
There are multiple data architecture frameworks that organizations can choose from, including:
This framework provides a structured approach to data architecture design by considering six dimensions of data: who, what, where, when, why, and how.
This framework is based on a hub-and-spoke model and is designed to support large, complex data architectures that need to be flexible and scalable.
This framework is designed to support data warehousing and business intelligence systems and is based on a bus-based data model.
This framework is focused on the governance and management of data and includes guidelines and best practices for areas such as data ownership, data quality, and data security.
Data architecture frameworks provide a structured approach to designing and organizing a data architecture and can be helpful for organizations that are looking to improve the management and use of their data.
- The Data Management Body of Knowledge (DAMA-DMBOK2) is a data management framework and reference guide created by DAMA International, a professional association for data managers.
- TOGAF was created in 1995. It is an enterprise architecture framework and methodology that includes a section on data architecture design and roadmap development.
- Meant to serve as the basis for an architecture, the Zachman Framework is an ontology framework that uses a 6-x-6 matrix of rows and columns to describe an enterprise architecture and data elements but does not include an implementation methodology.
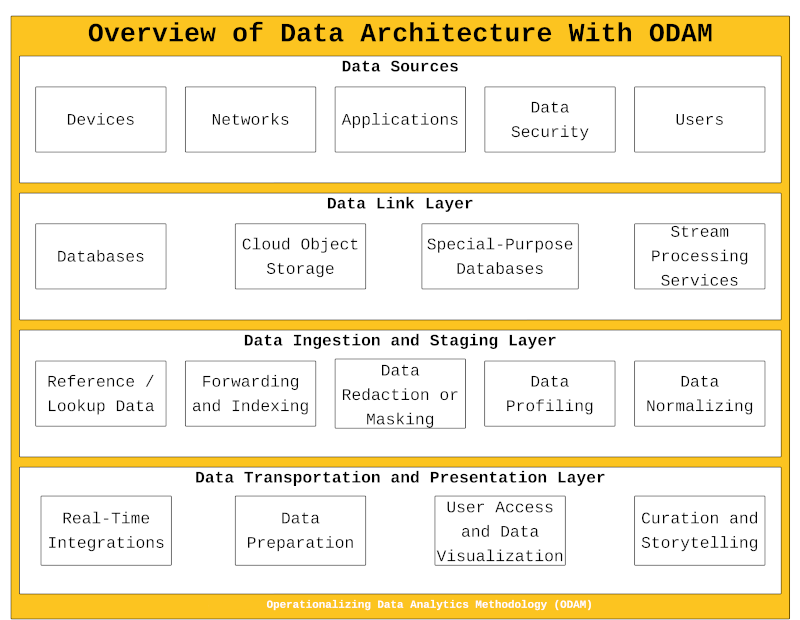
Using ODAM, organizations can ensure that data is flexible, adaptable, and elastic. ODAM provides the foundational components of a data strategy that your organization can customize and tailor to your business and specific needs. Components built-in to ODAM include:
- A guide to implementing a modern data architecture.
- Assistance in setting up agile data governance practices.
- Assistance in adopting and utilizing data integration and transformation tools.
- Guidance on implementing data virtualization.
- A framework to set up regular monitoring and optimization of data performance.
These strategies, when implemented in combination, can help organizations to improve the flow and use of data, making it more scalable and responsive to changing business needs.
#
Maintaining Data Quality
Maintaining data quality is the process of ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. This includes verifying the accuracy of data, correcting errors or inconsistencies, and removing or de-duplicating duplicate or outdated data. Data quality is an important aspect of data management, as it helps to ensure that data is reliable and can be used effectively for business purposes.
Poor data quality can lead to a variety of problems, such as incorrect or incomplete insights, wasted time and resources, and damage to an organization's reputation. To maintain data quality, it is important to establish and implement processes for regularly reviewing and cleaning data, as well as for verifying the accuracy of data as it is collected and entered into systems.
In terms of data architecture, data quality should be considered when designing and implementing data storage and processing systems. This may include implementing data validation and error correction mechanisms, as well as regularly reviewing and cleaning data to ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date. Maintaining data quality is an ongoing process that requires ongoing attention and resources, and should be an integral part of an organization's data management strategy.
#
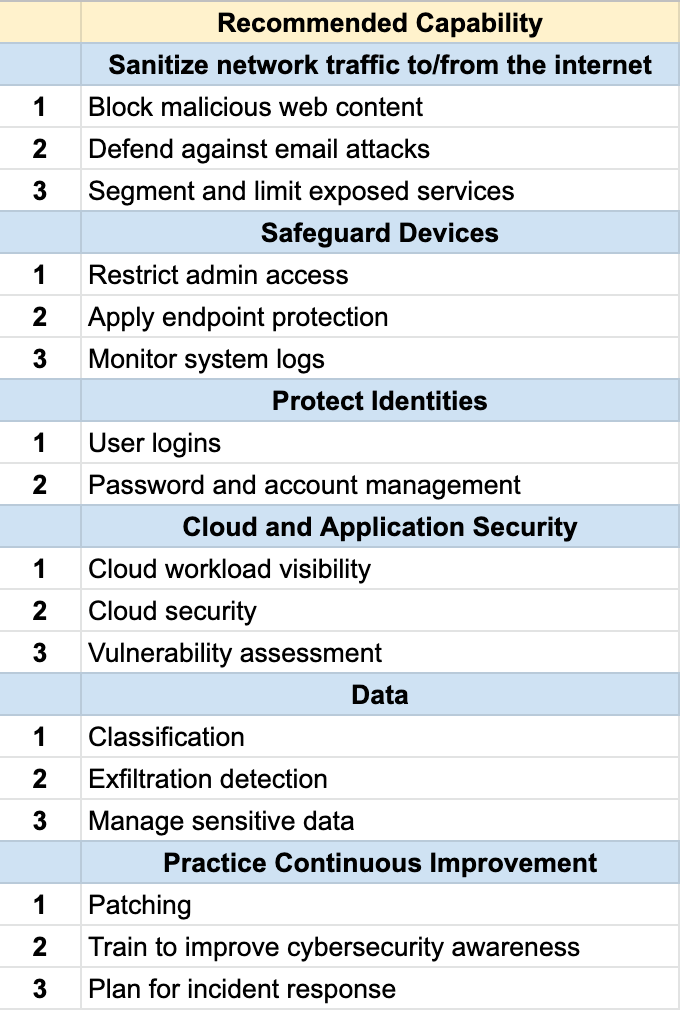
IT Assets, Networks, Applications, and Users
Monitoring IT assets is a crucial part of managing and maintaining a strong and secure technology infrastructure. By monitoring IT assets, organizations can identify and address issues as they arise, and ensure that their systems are functioning optimally.
Continuously monitoring the IT network for threats can provide a range of benefits to organizations. By continuously monitoring the IT network for threats, organizations can identify and address potential vulnerabilities or threats, enhance their threat visibility, improve their incident response capabilities, and reduce risk.
Continuously monitoring applications can provide a range of benefits to organizations. By continuously monitoring applications, organizations can identify and address issues that may be impacting system performance, enhance security, improve incident response capabilities, and reduce risk.
Organizations can anticipate increased user productivity and security, maintain regulatory compliance, protect sensitive data and prevent data breaches, and speed up incident response time by continuously monitoring users, identities, and access.
