#
Expected Outcomes and Goals for an ACE
Part III
"Our dilemma is that we hate change and love it at the same time; what we really want is for things to remain the same but get better."
— Sydney J. Harris, Journalist and Author
It's natural to have mixed feelings about change, as it can bring both opportunities and challenges. However, the desire to improve and make things better is a common and important goal for many organizations.

There are many things organizations and individuals can do to make things better. The question is: what motivates organizations and you to make change, challenge the status quo, and take action? For me and many others, there is plenty of motivation when I think of what the impact of the solution will be.
The impact of a data analytics program is likely to depend on a number of factors, including the quality and relevance of the data, the design and layout of the dashboard or report, and the intended audience and purpose.
#
Setting Your Intention and Achieving Success
Define clear objectives and goals: It is important to define clear objectives and goals for the data analytics program, so that the team knows what they are working towards and can measure their progress. This may involve setting specific targets or milestones, such as reducing the mean time to detect (MTTD) or mean time to respond (MTTR) to threats, or improving the accuracy of threat detections.
Identify the data sources and tools needed: In order to achieve success in the areas listed, it is important to identify the data sources and tools that will be needed to support the program. This may involve evaluating and selecting data analytics platforms, such as Splunk, as well as identifying the specific data sources that will be used to support the program.
Develop a clear strategy and roadmap: It is important to develop a clear strategy and roadmap for the data analytics program, so that the team knows what steps need to be taken to achieve their objectives and goals. This may involve identifying the specific processes and procedures that will be followed, as well as the technologies and tools that will be used.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement: To achieve success in the long term, it is important to foster a culture of continuous improvement within the data analytics program. This may involve regularly reviewing and analyzing the program's performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes as needed to ensure that the program is meeting its objectives and goals.
These recommendations can help people who are responsible for an organization's data analytics program to set their intention and achieve success in the areas of data collection and correlation, detection, monitoring, threat hunting, triage, investigations, and incident response.
What successful outcomes look like:
- Set up a SOC
- More Visibility into Endpoints
- Reduce Risk
- Replace Legacy tools
- Offering Splunk as a Service
- Maturing the SOC
- Reducing MTTI/MTTR
- Monitoring Services/Critical Applications/Network Monitoring
- Replacing Legacy Tools
- Offering Splunk ‘as-a-service’ to subordinate agencies or entities (e.g. multiple agencies within a State)
#
Understanding Analytics Maturity
Begin With Evaluating Your Organization's Capabilities
Analytics maturity refers to the level of capability, expertise, and sophistication that an organization has in using data analytics to support its mission and objectives. The structure of analytics maturity is typically understood in terms of a hierarchy or progression of increasing capabilities, with each level building on the insights and capabilities of the previous level.
There are many different frameworks and models that have been developed to understand and measure analytics maturity, and the specific categories and definitions may vary depending on the context and perspective. Here are a few common approaches to understanding analytics maturity.
These models typically define a set of stages or levels of analytics maturity, and may include categories such as "ad hoc" or "reactive," "repeatable," "strategic," and "advanced." These models typically describe the characteristics and capabilities of organizations at each stage of analytics maturity, and provide guidance on how to progress from one stage to the next.
These frameworks typically define a set of domains or areas of focus that are important for analytics maturity, and may include categories such as data governance, data management, data analytics, and data visualization. These frameworks typically describe the key practices and capabilities that organizations need to develop in each domain in order to achieve analytics maturity.
These assessments are designed to help organizations understand their current level of analytics maturity, and to identify areas for improvement. These assessments may involve self-assessment tools, interviews with key stakeholders, or other methods of gathering data and insights.
Analytics maturity is an important concept that helps organizations to understand their current capabilities and strengths in using data analytics, and to identify areas for improvement and development.
#
Assessing Your Current Data Analytics Maturity Level
By utilizing ODAM, organizations can efficiently and effectively move through the five levels of data analytics maturity, and ultimately reach the optimized stage where they are consistently achieving measurable business outcomes through their data analytics efforts.
The five levels of data analytics maturity within an organization.
At this stage, the organization is just starting to explore data analytics and has little to no infrastructure or processes in place. The organization is primarily focused on identifying potential use cases and building basic understanding of data analytics concepts.
At this stage, the organization has established some basic infrastructure and processes for data analytics, but is still in the early stages of implementation. The organization is primarily focused on building foundational capabilities such as data governance and data integration.
At this stage, the organization has established a mature data analytics infrastructure and has implemented a range of data analytics use cases. The organization is focused on expanding the use of data analytics across the organization and building advanced capabilities such as machine learning and predictive analytics.
At this stage, the organization has fully integrated data analytics into its business operations and has a mature data analytics culture. The organization is focused on driving business value and continuous improvement through advanced data analytics techniques and technologies.
At this stage, the organization has fully optimized its data analytics operations and is consistently achieving measurable business outcomes. The organization is focused on driving innovation and exploring new technologies to stay ahead of the curve.
- What are the primary business problems or goals that you are trying to solve with data analytics?
- What are the main challenges or pain points that your organization is currently facing in terms of data analytics?
- How is data currently being used across different departments and business functions within your organization?
- What types of data are you currently collecting, storing, and analyzing?
- How is data quality and governance being managed within your organization?
- What types of data analytics tools and technologies are currently being used within your organization?
- How is data analytics currently being integrated into your organization's decision-making processes?
- How is data analytics currently being used for strategic planning and forecasting within your organization?
- What is the current level of data literacy and skills within your organization?
- What are the current performance metrics and KPIs that are being used to measure the success of your data analytics initiatives?
It is important to ask these discovery questions and take a self-assessment of an organization's data analytics maturity because it provides a clear understanding of the organization's current capabilities, strengths, and areas for improvement. By understanding where an organization currently stands in terms of data analytics maturity, you can begin to identify and prioritize the areas that will have the greatest impact on their business outcomes. Furthermore, it allows for a realistic and actionable strategy to be developed for the organization to evolve their data analytics capabilities.
#
Take the Data Analytics Maturity Self-Assessment today!
The ODAM data analytics maturity self-assessment tool is a powerful resource for organizations looking to evaluate their current level of data analytics maturity. The assessment includes 50 questions, with 10 questions dedicated to each of the five levels of data analytics maturity. The self-assessment is an important step in the ODAM process as it helps organizations identify their current strengths and weaknesses, and provides a clear roadmap for how to improve their data analytics capabilities. By taking the self-assessment, organizations will be able to understand where they stand in terms of data analytics maturity and how to move forward with a strategic plan. The self-assessment tool is an easy way to start the journey of operationalizing data analytics, and it is a great starting point for any organization looking to take advantage of the power of data analytics.

#
Self-Service Analytics
Self-service data analytics is a type of data analytics approach in which users are able to access, analyze, and visualize data without the need for specialized technical skills or assistance from IT or data analysts. In a self-service data analytics environment, users typically have access to data analytics tools and platforms that are easy to use and allow them to explore data and create reports and visualizations without the need for coding or other technical expertise.
Self-service data analytics is designed to enable organizations to more quickly and easily gain insights from their data, and to enable users to more easily access and analyze data to support their decision-making and problem-solving. It is often used in conjunction with other types of data analytics approaches, such as centralized data analytics or business intelligence, to provide a more flexible and scalable approach to data analytics.
Self-service data analytics is designed to enable organizations to more easily and effectively leverage their data assets to support their mission and objectives.
#
Maximizing Value and Minimizing Risk
How ODAM Can Help Your Organization
ODAM helps organizations reduce risk by providing a clear set of steps and guidelines for planning, implementing, and managing data analytics projects. This structured approach helps to ensure that projects are well-defined and that all necessary steps are taken to ensure their success.
ODAM also helps organizations reduce risk by providing guidance on how to identify and prioritize the most important business needs and objectives, and how to align data analytics efforts with those needs. This helps organizations to focus on the most important data analytics projects and avoid wasting resources on less important or less valuable projects.
Finally, ODAM assists organizations in reducing risk by guiding them through the process of identifying and managing potential risks and challenges that may arise during the course of a data analytics project. Identifying potential sources of risk, developing contingency plans, and monitoring and managing risk throughout the project are all part of this. Organizations can reduce risk and increase the likelihood of success for their data analytics projects by adhering to the ODAM principles.
#
Risk as a Factor
The FAIR (factor analysis of information risk) approach is a framework for understanding, analyzing, and managing cyber risk. It is based on the idea that risk should be understood and managed in a consistent and objective way, using a common language and set of principles.
The FAIR approach is based on five key principles:
- Risk is a function of the likelihood of an event occurring and the impact of that event.
- Risk should be measured in terms of loss exposure, which is the potential financial impact of a risk event.
- Risk assessment should be based on objective and quantifiable data, rather than subjective opinions or assumptions.
- Risk management should be an ongoing process, rather than a one-time event.
- Risk management should be based on a consistent and repeatable process, using a common language and set of principles.
The FAIR approach provides a framework for understanding and managing cyber risk in a consistent and objective way, using a common language and set of principles. This can help organizations to better understand their risks and make informed decisions about how to manage those risks.
- What’s the asset/thing you’re trying to protect?
- Who is motivated to attack? Who might come after the asset? (Threat actors).
- How would they come after the asset?
- What’s the impact if the attacker is successful?
- What is the scope of the risk scenario and what is the risk statement?
The word impact means different things to different people. For instance, negative impacts to private businesses are different from those of the impacts to county governments. If a ransomware event happens in a business, the impact could be lost revenue and lost productivity. If a ransomware event happens in a county, terrible, life-threatening circumstances can arise. County’s usually operate jails and other essential services like (e)911. If a ransomware attack prevents doors from opening or phone lines to ring, people could lose their lives.
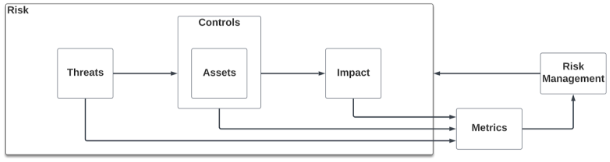
Over the last decade I’ve observed many ways and attempts of describing risk, priority, and worst case scenarios. In other words, there are many ways of describing risk, priorities, and what ifs. The cybersecurity field has many approaches and offerings that try to solve this problem (i.e., lack of a common language) but are still falling short.
How can we simplify things so that everyone with the organization can have an ample understanding of cybersecurity but more specifically, an understanding of how priorities are established. I’m a big believer in the “show your work” phrase we learned in elementary school when practicing math. Organizations should be able to quickly and easily show what pieces of technology and process are relevant to their mission and what data was used to derive findings.
To that end, I believe that organizations that take a methodical approach to identifying IT infrastructure (hardware and software) and processes relevant to the mission are more successful in keeping things secure, available, and free from issues. This first step - gathering a basic inventory - lays the foundation for building a resilient operation within your organization.
This first step
Gathering a basic inventory - lays the foundation for building a resilient operation within your organization.
#
"IT Governance Alignment
When you say that your goal is to align with IT governance, it means that you want to ensure that the analytics center of excellence (ACE) aligns with IT governance policies, processes, and practices of the organization. IT governance refers to the overall framework and approach that an organization uses to manage and control its IT assets and resources, and to ensure that they support and align with the objectives and goals of the organization.
Aligning the ACE with IT governance can help to ensure that the ACE is able to effectively support the mission and objectives of the organization, and that it is able to operate in a way that is consistent with the organization's IT policies and practices. This may involve ensuring that the ACE adheres to the same security, privacy, and compliance standards as other IT assets and resources, and that it is integrated into the organization's IT infrastructure and processes.
Aligning the ACE with IT governance can help to ensure that the ACE is able to effectively support the needs of the organization, and that it is able to operate in a way that is consistent with the organization's IT policies and practices.
#
Data Governance Alignment
Aligning the ACE with data governance can help to ensure that the ACE is able to effectively support the mission and objectives of the organization, and that it is able to operate in a way that is consistent with the organization's data policies and practices. This may involve ensuring that the ACE adheres to the same data quality, security, privacy, and compliance standards as other data assets and resources, and that it is integrated into the organization's data infrastructure and processes.
Aligning the ACE with data governance can help to ensure that the ACE is able to effectively support the needs of the organization, and that it is able to operate in a way that is consistent with the organization's data policies and practices.
#
Business Strategy Alignment
Aligning the ACE with the business strategy can help to ensure that it is able to effectively support the mission and objectives of the organization, and that it is able to contribute to the organization's success. This may involve ensuring that the ACE is focused on the right priorities and goals, and that it is able to provide value and insights that support the organization's business strategy.
Aligning the ACE with the business strategy can help to ensure that you are able to effectively support the needs of your organization, and that it is able to contribute to the organization's success.
#
Communication of Services Offerings and Capabilities
Here are some recommendations for the best way to communicate and describe data analytics services or capabilities:
- Clearly define the problem or opportunity that the data analytics service or capability is designed to address: Start by clearly defining the problem or opportunity that the data analytics service or capability is designed to address. This will help to provide context and relevance for the service or capability, and will make it easier for users to understand how it can be applied.
- Describe the key features and capabilities of the service or capability: Next, describe the key features and capabilities of the service or capability. This may include the types of data that it can analyze, the types of insights or outputs that it can provide, and any other key features or functionality that make it unique or valuable.
- Explain how the service or capability can be used: Clearly explain how the service or capability can be used, including any specific steps or processes involved. This will help users to understand how they can leverage the service or capability to address their needs or goals.
- Provide examples of how the service or capability has been used successfully: Provide examples of how the service or capability has been used successfully in the past. This will help users to better understand the potential value and applications of the service or capability, and will help to build confidence and trust in its capabilities.
- Clearly communicate any requirements or limitations of the service or capability: Clearly communicate any requirements or limitations of the service or capability. This will help users to understand any constraints or limitations that they may need to consider when using the service or capability, and will help to manage expectations.
#
Evangelism of Data Literacy and Data Analytics
The phrase "evangelism of data analytics and data literacy" refers to the act of promoting and advocating for the importance and value of data analytics and data literacy within an organization. This includes educating employees and stakeholders about the benefits and applications of data analytics, and helping to build awareness and understanding of data literacy concepts and skills.
Data analytics refers to the process of collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to generate insights and inform decision-making. Data literacy refers to the ability to understand and use data effectively, including the ability to read, work with, analyze, and communicate data.
Evangelism of data literacy and data analytics includes providing training and education on data analytics and data literacy concepts, promoting the use of data analytics and data literacy tools and techniques, and advocating for the importance of data analytics and data literacy within the organization.
The goal of evangelism of data literacy and data analytics is to help organizations to more effectively leverage their data assets to support their mission and objectives, and to help employees and stakeholders to develop the skills and knowledge they need to use data effectively.

#
The 3 Cs of Data Literacy
Jordan Morrow, a data literacy expert, identified the three Cs of data literacy: curiosity, creativity, and critical thinking. These three traits are essential for individuals to have in order to effectively work with and understand data. Morrow believes that by fostering these qualities in individuals, they are better equipped to approach data with a curious and open mind, generate creative insights, and think critically about the data they are working with.
- Creativity is the ability to generate original and innovative ideas, and it is an important aspect of data literacy because it allows individuals to approach data with a fresh perspective and to find new and creative ways to analyze and interpret it. By being creative with data, individuals can be more likely to uncover new insights and identify opportunities that may not be immediately apparent. Creativity can also help individuals to see data in a different light, enabling them to discover new patterns and trends and make connections that might not have been previously considered. Overall, creativity is an essential component of data literacy that helps individuals to think creatively, explore new ideas, and find novel solutions to complex data problems.
- Curiosity is a key aspect of data literacy. It drives individuals to seek out new information and to explore different data sources and perspectives. Being curious about data can help individuals to ask the right questions and to look for patterns and trends that might not be immediately obvious. This, in turn, can lead to new insights and a deeper understanding of the data.
- Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and evaluate data in a logical and systematic manner, including considering the sources, quality, and implications of the data. This skill is essential for making informed and sound decisions based on data.
#
The Four Levels of Data Analytics
Jordan Morrow also defined the four levels of analytics as descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. These levels describe the increasing complexity and sophistication of data analysis, from simply describing what has happened in the past, to predicting future outcomes and prescribing actions based on those predictions.
This level of data analytics involves summarizing and describing data, and may include activities such as generating reports, calculating totals and averages, and creating charts and graphs.
This level of data analytics involves investigating data to identify patterns and trends, and may include activities such as identifying correlations and causes, and using data mining techniques to uncover hidden insights.
This level of data analytics involves using data and statistical models to make predictions about future outcomes or events, and may include activities such as building predictive models, forecasting future trends, and simulating scenarios.
This level of data analytics involves using data and analytical insights to recommend specific actions or decisions, and may include activities such as optimization, simulation, and decision-making support.
These four levels of data analytics represent a hierarchy of increasing complexity and sophistication, with each level building on the insights and capabilities of the previous level.
Exploratory data analytics typically refers to the process of examining data in order to discover patterns, trends, and insights that might not be immediately apparent. This process may involve using various techniques and tools to visualize and analyze data, and to identify relationships and correlations within the data.
Note
Exploratory data analytics is an important aspect of data analysis, as it can help organizations to better understand their data, to identify trends and patterns that might not be immediately apparent, and to generate insights and ideas that can inform decision-making and problem-solving.
In terms of the levels of data analytics that I described earlier, exploratory data analytics could be considered to fall under the category of diagnostic analytics. This approach to data analytics often involves investigating data to identify patterns and trends, and advanced techniques. For example, identifying correlations and causes or using data mining techniques to uncover hidden insights.
#
Data Analytics Support and Consulting Services
The ACE offers a variety of support and consulting services to help organizations effectively utilize data analytics in their operations. These services may include:
- Developing a data analytics strategy that aligns with business goals and objectives, and outlining the roles, responsibilities, and processes required for its implementation.
- Providing training and education to enhance employees' data literacy, visualization, and analysis skills.
- Establishing best practices and frameworks for data analytics, including approaches to data collection, analysis, and visualization, and standardizing data analytics processes across the organization.
- Managing data analytics projects, including defining project scope and objectives, managing resources, and tracking progress and outcomes.
- Offering expert guidance and consultation on data analytics projects, including identifying appropriate data sources, developing analysis plans, and providing technical support.
The ACE is a valuable resource for organizations seeking to effectively utilize data analytics to achieve their objectives.
#
Best Practices and Standards in Data Analytics
The ACE plays a crucial role in helping organizations to adopt and adhere to best practices and standards in data analytics. Best practices are generally accepted guidelines or approaches that are considered to be the most effective or efficient way of achieving a particular goal, while standards provide a basis for comparison or evaluation and can help to ensure that data analytics projects and initiatives are aligned with industry standards.
By providing guidance on best practices and standards management, the ACE can help organizations to ensure that their data analytics initiatives are based on a solid foundation of technical, methodological, and organizational principles. This may involve providing training and education on best practices and standards, developing and promoting guidelines and frameworks for data analytics, and helping to identify and implement appropriate standards and protocols for data analytics projects and initiatives.
Adopting and adhering to best practices and standards can help organizations to more effectively leverage data analytics to support their mission and objectives, and to ensure that their data analytics initiatives are aligned with industry standards and best practices. By working with the ACE, organizations can ensure that they have the necessary tools, resources, and expertise to effectively manage their data analytics initiatives and achieve their desired outcomes.
#
Data Analytics Training and Enablement Services
The ACE is responsible for providing training and enablement services to help organizations develop the skills and knowledge they need to effectively use data analytics to support their mission and objectives. This may include in-person training sessions, online courses and workshops, webinars, and other educational resources. The content and format of the training and enablement services will be tailored to the needs and goals of the organization and the level of expertise of the employees receiving the training. By providing these services, the ACE helps organizations to improve their data literacy, enhance their data analysis and visualization skills, and become more proficient in using data analytics to drive business decisions and outcomes.